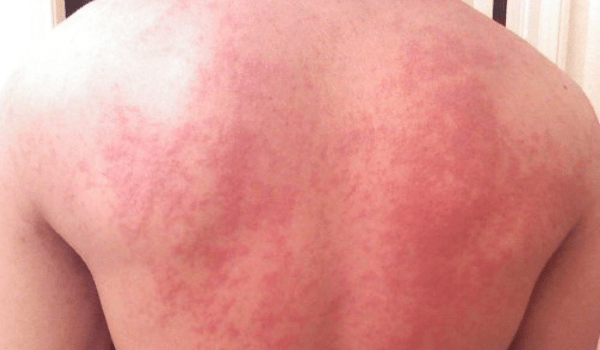
While you may have heard of, or even had, hives before, there are many things about them and three hives symptoms everyone should be aware of. Hives, or urticaria, appear suddenly as pale red bumps or plaques on the skin. Let’s dive into causes, symptoms, and more.
What is causing my hives?
Hives are usually a reaction to some type of allergen, such as peanuts or other food, medication, pets, and insects or even an unknown reason. Other well-known aggravates of hives include sun exposure, stress, and exercise.
Hives symptoms can occur immediately following exposure to any of the above irritants, or symptoms may not appear for up to two hours following exposure. Even though hives are a common skin condition we treat, not everyone is able to identify the symptoms. Here are a few common hives symptoms.
Three hives symptoms
-
Red Welts
Red welts are one of the most common hives symptoms that are easily recognized. Although the welts typically present as red, they can also be flesh colored. These welts can appear anywhere on the body. Welts can occur alone or in a group and may fade and reappear, possibly changing shapes and size, as the reaction continues.
-
Angioedema/Swelling
Angioedema is characterized by large welts that appear under the skin. This intense swelling can occur in addition to welts. The eyes and lips are typically the areas of the body that are affected by angioedema, but angioedema can also affect the throat, hands, and feet. In areas that are affected by angioedema, you may feel warmth radiating from that specific area. Less intense swelling can also occur. If you believe you may be experiencing angioedema, we recommend that you seek medical treatment immediately.
-
Itching
Hives symptoms also include itchy skin. This itching can be minor to severe, possibly causing pain. Itching is not only irritating but can lead to tears in the skin, which can lead to infection. In addition to this itching, you may feel a stinging sensation. While it may be difficult, it is best not to scratch the affected areas.
How long does it take for hives to go away?
With acute urticaria, hives last no more than six weeks, if not less. In common cases, they may disappear within 24-48 hours. Usually certain foods, medications, infections, or insect bites may cause this type of hives.
However, if your symptoms last more than six weeks, you may have a case of chronic urticaria, or chronic hives. This type may be more difficult to identify and determine the causes. In some cases, it can be caused by infection, hepatitis, thyroid disease, or cancer.
When should you see a doctor for hives?
Although you can usually treat mild cases of hives at home, you should see a doctor if your outbreak doesn’t disappear within a few days. In severe cases, if you feel your tongue, lips, mouth or throat swelling or if you’re having trouble breathing, you should seek emergency care immediately. Although rare, there is a possibility that anaphylactic shock may accompany hives symptoms. Anaphylactic shock is a severe allergic reaction that is characterized by shortness of breath and a sudden and severe drop in blood pressure and should be acted on quickly.
Diagnosing hives
Dermatologists can diagnosis hives by examining your skin and taking a history of your symptoms. Understanding the cause of hives, however, can be a bit more complicated. Allergy tests, blood tests, and skin biopsies can be used to test for hives. In addition to testing, your dermatologist may ask that you keep a journal of your food intake, activities, and stress levels to monitor if any of these factors affect your hives symptoms. However, even with testing, a cause may not be found, especially if the hives symptoms have occurred for longer than six weeks.
How do I treat hives?
Not only is recognizing hives symptoms important but understanding and knowing the possible treatment options helps you to become an advocate for yourself. Most mild cases of hives are treated by a non-drowsy, over-the-counter antihistamine, such as Benadryl. Antihistamines can also be prescribed to take daily for chronic hives symptoms, helping to prevent hives from occurring. Other medications used to treat hives symptoms include corticosteroids and antibiotics. All of these medicines can help relieve the itching and swelling.
For chronic cases of hives, Omalizumab, an injectable medicine, can be used to treat hives symptoms in addition to the use of antihistamines. For cases of hives with areas of angioedema, a shot of epinephrine under the skin may be required. In addition to medications, you can also relieve itching and swelling by placing a cool cloth on the affected areas or taking a cool shower.
Are you dealing with hives symptoms? Contact Vujevich Dermatology Associates today at 412-429-2570 to make an appointment at one of our three offices in the greater Pittsburgh area. Vujevich Dermatology Associates offers medical, surgical, and cosmetic dermatology from some of the most highly trained physicians and clinicians in the greater Pittsburgh area. You can also follow us on Facebook to see what’s new in the world of dermatology.